How Are Differences in Properties Among the Transition Elements Explained
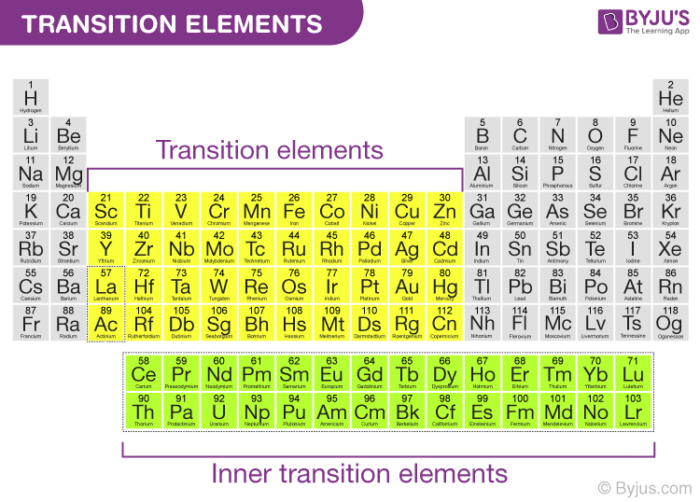
The elements with incompletely filled d-subshell in their ground state or most stable oxidation state are named as D-block elementsThey are additionally named as transition elementsThe partially filled subshells incorporate the n-1 d subshellAll the d-block elements have a similar number of electrons in. This happens as each additional electron enters the penultimate 3d shell.
Transition Elements General Properties And Trends With Faqs
While the term transition has no particular chemical significance it is a convenient name by which to distinguish the similarity of the atomic structures and resulting properties of the elements so.
. The properties of transition elements are as follows. Explain why some metals can act as permanent magnets. The transition metals are more electronegative than the main group metals for example and are therefore more likely to form covalent compounds.
The difference between representative elements and transition elements is that representative elements are the chemical elements in the group 1 group 2 and in the groups from 13 to 18 whereas transition elements are chemical elements in group 3 to group 12 including Lanthanides and Actinides. As can be seen from their reduction potentials see Appendix H some transition metals are strong reducing agents whereas others have very low reactivity. Groups are numbered 118 from left to right.
What is the properties of transition elements. The definition of transition metals and an explanation of their electron configurations can be found on the transition metals page. Theyre excellent conductors of electricity.
This page looks at the uses of transition metals and covers their uses as metals compounds and catalysts. How can a transition metal form an ion with a charge of 3 or higher. Explain how a metal can become a temporary magnet.
This colour is explained by the d-d transition of electrons. Introduction to General Properties of the Transition Elements. The transition elements therefore exhibit many oxidation states.
However the atom sizes of the elements in the third transition series are virtually the same as those of. The peripheral shell configuration of these elements is ns 2. Compared to other metals most transition metals have.
Another difference between the main group metals and transition metals can be seen in the formulas of the compounds they form. There is a relatively low gap in energy between the possible oxidation states of these elements. They can form several states of oxidation and contain different ions.
Identify three ways transition metals are separated from their ores. Elements in the same group of the periodic table have similar chemical properties. High melting point group 1 metals have low melting points hard group 1 metals are soft high density group 1 metals have lower densities Chemical properties.
Elements can be classified as metals metalloids and nonmetals or as a main-group elements transition metals and inner transition metals. These properties of the transition elements are listed below. All transition elements exhibit similar properties because of the identical electronic configuration of their peripheral shell.
For example the lanthanides all form stable 3 aqueous cations. Some properties of transition elements are different from those of the metals in group 1. In other words they have d1 to d9 electrons.
However they are also considered as transition metals because they have similar properties to those of transition metals. Transition metal any of various chemical elements that have valence electronsie electrons that can participate in the formation of chemical bondsin two shells instead of only one. Group 1 metals and transition metals are different from each other mainly based on the colour of the chemical compounds that they form.
For example elements on the left in groups 1 2 and 13 are going. How are differences in properties among the transition elements explained. Use as metals The properties of transition metals are very similar to the properties of normal metals so Im.
Inner transition elements are in the f-block and in the f-orbital have valence electrons. These elements form coloured compounds and ions. This creates an effective shield between the nucleus and the outer 4s shell.
They have to properties of metals. They have a low energy gap between the oxidation states of the elements. I The atomic sizes of the elements of the first transition series are smaller than those of the heavier elements of 2nd and 3rd transition series.
The properties of the elements of the first transition series differ from those of the heavier transition elements in many ways. The three main differences are. Because the main group elements consist of both metals and nonmetals their physical properties are going to be quite different.
They form coloured ions and compounds and this can be explained due to the d-d transition in electrons. Transition metals are the d -block elements and they have incompletely filled d -orbitals. Properties of the Transition Elements Transition metals demonstrate a wide range of chemical behaviors.
Are isotopes different in. The general properties of the. The maximum oxidation states observed for the second- and third-row transition metals in groups 38 increase from 3 for Y and La to 8 for Ru and Os corresponding to the formal loss of all ns and n 1d valence electrons.
The d10 metals namely Zn Cd and Hg have completely filled d -orbitals. The key difference between group 1 metals and transition metals is that the group 1 metals form colourless compounds whereas the transition metals form colourful compounds. These elements express many oxidation states.
1Definition of Representative Element. The transition elements are in the d-block and in the d-orbital have valence electrons. The second- and third-row transition metals behave similarly but with three important differences.
They are the Lanthanides and the Actinides.
Difference Between Transition Metals And Inner Transition Metals Definition Properties In Relation To Electronic Configuration
Difference Between D Block Elements And Transition Elements Definition Properties Examples

Difference Between Group 1 Metals And Transition Metals Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
No comments for "How Are Differences in Properties Among the Transition Elements Explained"
Post a Comment